I ate chocolate for the third time today.
Replace chocolate with your most recent pregnancy craving, and you have a recipe for potential disaster.

Pregnant moms usually have food cravings they seem to get enough of. However, if you are an expectant mom and you indulge yourself ever so often, maybe it’s time to look back on your diet and lifestyle. You may not be aware, but you are already putting yourself and your baby at risk for gestational diabetes.
Is this your first time hearing about gestational diabetes? You’re in luck. We put together the basics about gestational diabetes you should need to know.
What Is Gestational Diabetes?
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) or simply gestational diabetes puts many expectant mothers and their babies at risk. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), an estimated 1% to 14% of pregnancies are affected by gestational diabetes in the United States.
Gestational diabetes’ onset is usually in the later stages of pregnancy, which starts around the 24th week. While gestational diabetes recedes after pregnancy, there are significant effects of gestational diabetes on your child in the long-run.
What Causes Gestational Diabetes?
You might think that you are not at risk for gestational diabetes because you have a perfectly normal sugar level. Don’t be so sure! Many women had gestational diabetes, even if they had a healthy sugar level before their pregnancy.

Problems with glucose tolerance during pregnancy are one of the causes of gestational diabetes in expectant mothers. The hormones that support the placenta affect how insulin is used up by the body. This reaction caused by hormones leads to insulin resistance. Thus, expectant mothers have to use up more insulin in their bodies during pregnancy.
Symptoms Of Gestational Diabetes
If you are suspecting that you have pregnancy diabetes, here are some of the signs of gestational diabetes to look out for:

● Abnormal thirst
● Fatigue
● Frequent urination in large amounts (read more about it here: https://www.healthline.com/health/gestational-diabetes)
● Blurry vision
Risk Factors For Gestational Diabetes
● Maternal Age
Maternal age can also affect the development of gestational diabetes. A study conducted by Pons (2015) found out that women who were more advanced in age (35 years old and above) were more at risk for gestational diabetes complications.
● Family History
Having a family history of women with gestational diabetes and Type-2 diabetes also increases your risk of having gestational diabetes in your pregnancy.
● Race
Several studies point out that race affects the prevalence of pregnancy diabetes. Specifically, according to a research conducted by Fujimoto, Samoa, and Wotring in 2013, Hispanic-Americans, Asian-Americans, Pacific Islanders, and African-Americans have a higher risk for gestational diabetes as compared to their non-Hispanic white women counterparts.
Gestational Diabetes’ Effect On Your Baby
● Unusually Large Birth Weight
One of gestational diabetes’ effect on your child is macrosomia (high birth weight). Usually, these children have a birth weight beyond 9 pounds.
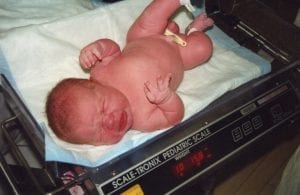
The excessive birth weight happens when the additional sugar enters the placenta. It then triggers your baby’s system to make more insulin to counter the sugar.
● Jaundice
Jaundice is the outward manifestation of high bilirubin levels in the bloodstream. Some symptoms of this include the yellowing of the skin and eyes.
If left untreated, jaundice can affect the development of your child’s cognitive function. It can also cause deafness or cerebral palsy.
● Hypoglycemia
Your child’s systems produce more insulin while in the womb. Hence, your child has an increased risk of hypoglycemia after delivery. Hypoglycemia occurs when blood sugar in the body is lower than average.
What Should You Do To Prevent Gestational Diabetes?
Prevention is definitely better than cure. If you can avoid having gestational diabetes, you and your child will be free from having pregnancy diabetes-related problems in the future.
● Go For Regular Check-Ups
Your obstetrician will monitor your sugar levels as well as your weight gain. To track your sugar level, your doctor will advise you to go for blood work to see the amount of sugar in your bloodstream. You also need to go for a check-up every month until your expected delivery date.
A 26-35 pound weight gain during pregnancy is considered normal. Anything beyond that is already a cause for alarm. Your child can have an increased risk of neural tube defects as a result of obesity during pregnancy.
● Eat Right
One of the sure-fire ways to avoid gestational diabetes is by watching your diet. If you’re one of those expectant mothers who have unhealthy cravings and indulge themselves often, better start ditching the sweets for more greens.

Incorporating more greens into your diet can help your body regulate the amount of sugar in your bloodstream. Adding at least one to two servings of fruits and vegetables for every meal or at least four servings of vegetables per day should do the trick.
● Exercise
Exercise is also one of the best ways to regulate the sugar levels of expectant mothers. Sweating out also helps your body eliminate extra toxins. Moreover, simple exercises can help you during your delivery. You will have less trouble in pushing out your baby.
Walking around the neighborhood every morning for 10 minutes can help you to stay active. You can also do easy household chores such as vacuuming the home or tending your garden. If you want, you can also enroll in specialized group exercises for expectant mothers. These include dance classes and water aerobics.
What Should You Do If You Already Have Gestational Diabetes?
● Diabetic Diet
People with diabetes follow a strict diet based on their glycemic goals for every meal. Your obstetrician can refer you to a dietitian well-versed in helping out expectant mothers suffering from gestational diabetes symptoms.
● Insulin Shots
Insulin shots are the only approved medication for gestational diabetes in America. They regulate the presence of insulin in your bloodstream according to your needs. Insulin shots can help maintain a healthy sugar level. It can then help you have a safe delivery.
In summary, gestational diabetes affects a significant portion of expectant American mothers and is, therefore, a pressing concern. The rising numbers of obesity and hypertension also add to the growing number of mothers with gestational diabetes. However, gestational diabetes can be prevented. With proper diet and exercise, expectant mothers can enjoy their pregnancy journey in peace.
FAQs
What are the warning signs of gestational diabetes?
Expectant mothers with gestational diabetes typically experience fatigue, lethargy, nausea after eating, blurred vision, and urge to urinate in severe levels. See a doctor if you have these signs.
Does diet cause gestational diabetes?
Yes, a diet can cause gestational diabetes. If you overeat carbohydrates and your body cannot produce enough insulin, your blood sugar levels will rise and turn you into a person with diabetes.
Does gestational diabetes go away?
Yes, gestational diabetes usually goes away after giving birth. However, it transitions into type 2 diabetes for some women.
Is gestational diabetes common in pregnancy?
Yes, gestational diabetes is common during pregnancy. Up to 5% of expectant mothers get diagnosed with it between the 24th and 28th weeks of pregnancy.
Can eating too much sugar cause gestational diabetes?
No, overeating sugar is not one of the primary causes of gestational diabetes. Diabetes is often hereditary, so you may be born with the genes that cause it. Still, you can cut back on carbohydrates to manage the disease.
What do I eat if I have gestational diabetes?
You need to look for healthier versions of your favorite foods. Stick with water instead of soda as well.
What can you not eat with gestational diabetes?
You cannot eat a lot of processed foods if you have been diagnosed with gestational diabetes. Even the foods that are not labeled as “sweet” contain sugar.
Can I eat cheese with gestational diabetes?
Yes, you can eat cheese in moderation with gestational diabetes because it is made up of salt and fat. Some experts recommend eating fresh cheeses to lower the risk of developing this disease.
What can I drink besides water with gestational diabetes?
You can drink apple cider, orange juice, and lemonade instead of water if you have gestational diabetes. You need not lay off hot chocolate or sweet tea either.
How can I lower my blood sugar during pregnancy?
One of the things that can lower your blood sugar pregnancy is avoiding junk foods. You should also exercise a few times a week, if possible.
What happens if you are diagnosed with gestational diabetes?
Gestational diabetes occurs when your placenta produces glucose-building hormones, and your pancreas cannot make enough amount insulin. Once it happens, you need to avoid increasing your blood sugar level by eating too many carbohydrates.
Can you have a small baby with gestational diabetes?
Yes, you can technically have a small baby if you get gestational diabetes. The silver lining is that it does not happen all the time.
Last Updated on January 11, 2023 by Rejie Salazar
DISCLAIMER (IMPORTANT): This information (including all text, images, audio, or other formats on FamilyHype.com) is not intended to be a substitute for informed professional advice, diagnosis, endorsement or treatment. You should not take any action or avoid taking action without consulting a qualified professional. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions about medical conditions. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking advice or treatment because of something you have read here a FamilyHype.com.
Your blog is so nice i read it carefully all information are good and helpful.i share your blog and information with my friends and different groups because your blog is so attractive.