Ovulation is a critical event in human reproduction, where an egg is released from the ovary, typically occurring 14 days before menstruation begins. This period marks the peak fertility phase for a woman, making understanding the ovulation cycle vital for anyone trying to conceive.
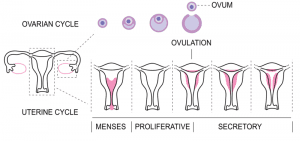
Ovulation Cycle Defined
In simple terms, ovulation is the process of releasing an egg from the ovaries, which occurs 14 days before the beginning of your period. The closer you get to the day of ovulation, the more fertile a woman is.
The ovarian cycle refers to the changes that take place in the ovary driven by pituitary hormones such as FSH and LH (follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone), primarily produced by the anterior pituitary gland. This cycle consists of three stages: the follicular phase, where primordial follicles develop into primary follicles and then mature under the influence of these hormones; the process called ovulation, where the mature follicle releases an egg; and the luteal phase, where the corpus luteum develops from the remnants of the follicle and produces estrogen and progesterone to prepare for potential fetal development.
Estrogen is the most common of the three ovarian hormones and accounts for the growth and development of female breasts. It is also the primary hormone that helps girls develop during puberty. Its main function in the ovulation cycle is to regulate one’s menstrual cycle.
Progesterone. It is primarily responsible for maintaining the safety and integrity of a woman’s pregnancy. It also aids in preparing the body for fertilization of the egg, which happens in the second half of the menstrual cycle. It thickens the uterine lining. Progesterone is also produced in the placenta during pregnancy.
Luteinizing hormone (LH). LH works together with progesterone and estrogen to regulate the menstrual cycle, but its most crucial role happens just before and during ovulation. These hormones multiply to elicit the release of the egg.
The Menstrual Cycle Explained
We will be able to better understand the ovulation cycle if we learn more about the menstrual cycle, also known as the reproductive cycle. Menstrual cycles vary, but on average, they last around 28 days. They consist of four phases, which we have listed below.
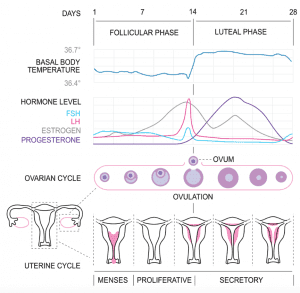
- Menstruation. This doesn’t need much explanation. Menstrual bleeding occurs here as a result of the shedding of the uterine lining. The phase takes 3 to 7 days. Menstrual periods happen after the progesterone levels drop.
- Follicular Phase. Follicular Phase. This phase has to do with follicular development. Making up for the shedding, the body undergoes redeveloping. The ovarian follicles start to grow due to the release of the follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). The follicles then produce progesterone, and estrogen levels increase, which helps thicken the uterine lining in preparation for possible fertilization. During this phase, a dominant follicle released begins to develop faster than the others. It then releases additional estrogen into your body. In the latter part of this phase, the release of the luteinizing hormone (LH) also occurs. LH and FSH production is caused by the pituitary gland.
- Ovulation Phase. In this phase, ovulation occurs. An ovarian follicle ruptures, and the mature egg moves down the fallopian tube after a surge of luteinizing hormones. After the ruptured follicle (the most mature follicle) releases the ovum, it thrives for about 6 to 12 hours. If cervical mucus is present, the sperm can also thrive for a few days, where it waits for the egg. This so-called fertile window may result in pregnancy.
- Luteal Phase. This is the last phase, which occurs right after ovulation and just before a woman’s menstrual period. The follicle that contained the egg (corpus luteum) produces progesterone and then softens the lining for the fertilized egg to ‘rest.’ This whole phase usually takes 12 to 16 days. This phase determines whether or not the egg is fertile or not. If implantation occurs, the human embryo produces human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), which can be detected by pregnancy tests.
Ovarian Cycle And Ovulation

However, if your cycles are shorter, like 24 days, for example, day ten would be the ovulation day, and the fertile window would be between the 7th and 10th day.
The Importance Of Ovulation
It can be devastating for some women and couples to find ways and means to conceive but to no avail. It would be heart-wrenching for loving couples who have been married for so long yet have not seen the fruit of their love and companionship. This is the reason why the importance of knowing about ovulation and the ovulation cycle must be emphasized.
The whole gamut about fertility can be complicated, but certainly, a simple understanding of ovulation and where it fits into the fertility process is relevant in utilizing your fertile days. A woman’s ovulation only has one goal, and that is pregnancy. So you should take some time and effort to know more about it. Dig a little more into this. Good luck!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
When Do You Ovulate?
Your ovarian cycle starts 14 days after your period. Some women, however, may ovulate as early as six days post-menstruation.
How Do I Calculate My Ovulation Day?
Count the number of days between the first days of your menstruation last month and this month. Then, subtract this number to 14 days.
What Are The Days You Can Get Pregnant?
There is a six-day window when you can get pregnant. It starts once your egg cell drops during the ovulation cycle.
Can You Get Pregnant When You’re Not Ovulating?
No, you cannot get pregnant when you’re not ovulating. In case you do not ovulate naturally, you may consult a fertility doctor to induce the release of a mature egg cell.
Is Ovulation Pain A Good Sign Of Fertility?
Yes, experiencing pain before menstruation is a great sign of fertility. Ovulation pain increases your chances of getting pregnant.
How Do You Tell If You Are Ovulating?
It is easy to tell if you are ovulating by checking the appearance of your vaginal discharge. The cervical mucus is more transparent and wetter than usual at this point.
Which Day After Your Period Is Best To Get Pregnant?
It is best to get pregnant approximately 14 days after your last menstruation. This is when the ovaries release the mature egg, which remains alive for up to 24 hours.
How Do I Know If I Am Fertile Enough To Get Pregnant?
You can start trying with your partner on the tenth day since your last period, as it is the beginning of your ovulation cycle. The increased amount of clear vaginal discharge is a sign of fertility.
How Can I Easily Get Pregnant?
The easiest way to get pregnant is by tracking your menstrual cycle to know when you are ovulating. If your period is irregular, it is best to consult a specialist to make it regular.
What Age Is A Woman Most Fertile?
A woman is most fertile in her early 20s. Once you reach the age of 25, the possibility of getting pregnant after a few months decreases by 20%.
Can You Ovulate Twice In One Month?
What Does Ovulation Discharge Look Like?
Can You Ovulate While On Your Period?
Why Did I Not Get Pregnant During Ovulation?
What Happens The Day You Ovulate?
Last Updated on May 10, 2023 by Bernadine Racoma
DISCLAIMER (IMPORTANT): This information (including all text, images, audio, or other formats on FamilyHype.com) is not intended to be a substitute for informed professional advice, diagnosis, endorsement or treatment. You should not take any action or avoid taking action without consulting a qualified professional. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions about medical conditions. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking advice or treatment because of something you have read here a FamilyHype.com.